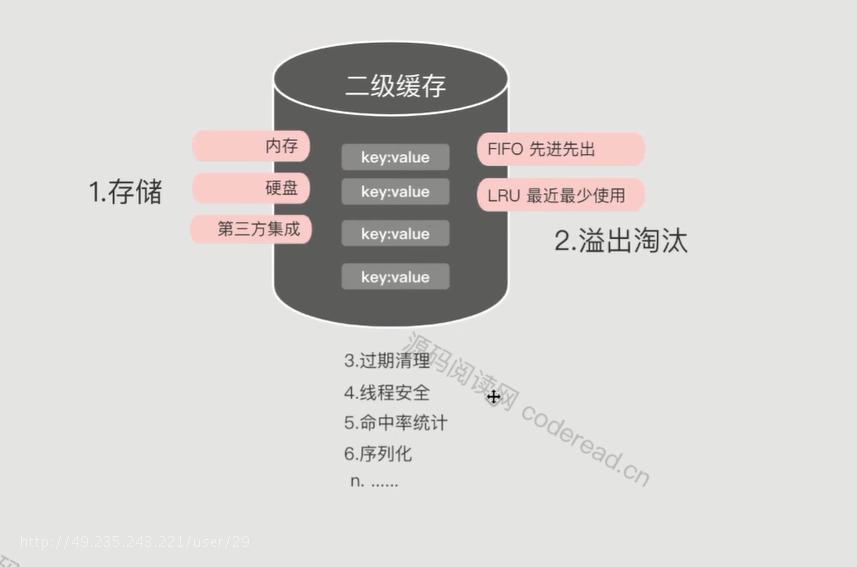
二级缓存定义与需求分析

二级缓存扩展性需求
FIFO:溢出淘汰算法(FastInFastOut先进先出)
先缓存的部分老数据清空,让新数据缓存起来
LRU:最近最少使用的数据清空
二级缓存组件结构
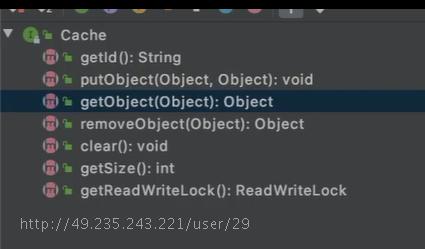
缓存Cache接口方法列表:
责任链模式
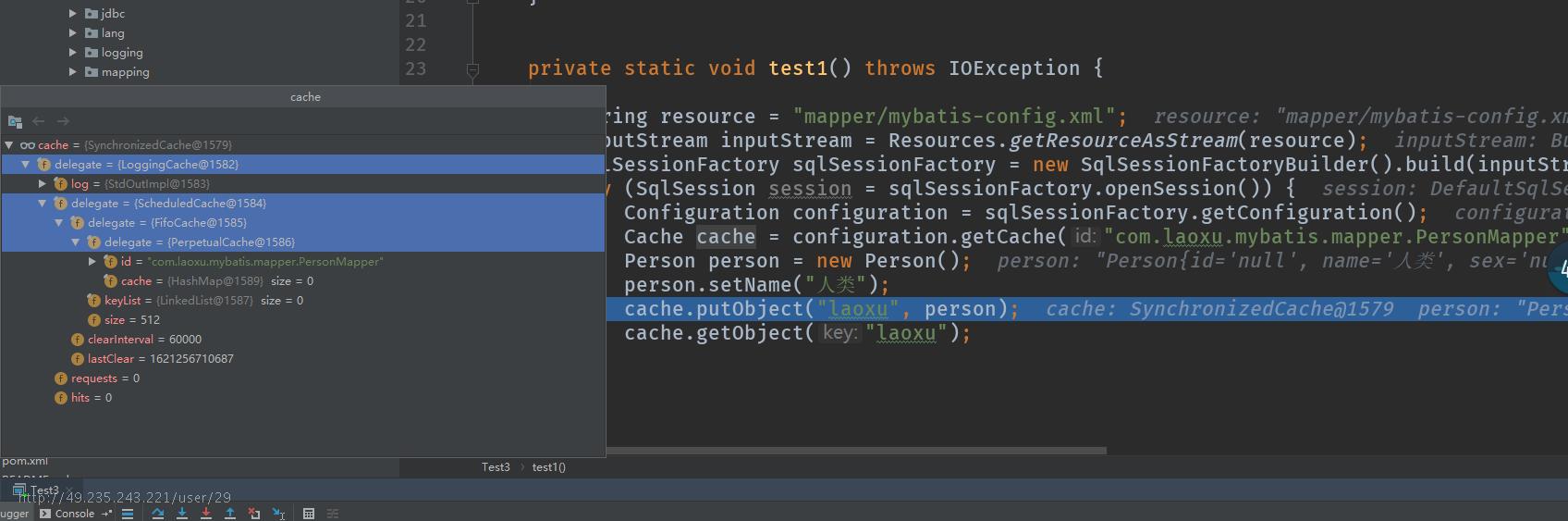
测试调用缓存接口:
private static void test1() throws IOException {
String resource = "mapper/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
Configuration configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
Cache cache = configuration.getCache("com.laoxu.mybatis.mapper.PersonMapper");
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("人类");
cache.putObject("laoxu", person);
cache.getObject("laoxu");
}
}
PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections. PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections. PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections. PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections. Cache Hit Ratio [com.laoxu.mybatis.mapper.PersonMapper]: 1.0
缓存命中率100%
装饰器缓存嵌套》责任链:
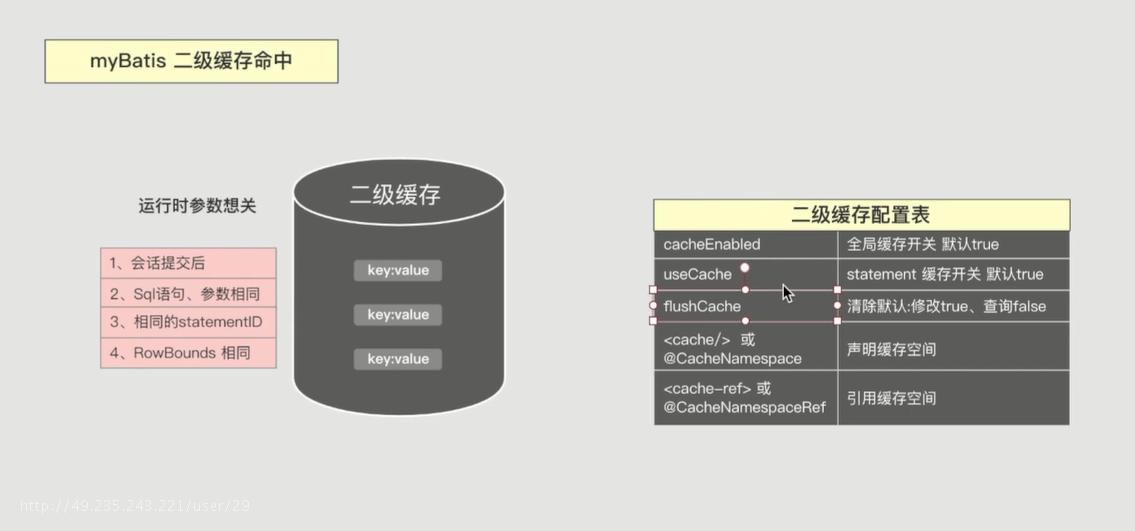
二级缓存配置表
全局缓存开关
mybatis-config.xml中配置,默认true开
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING" />
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true" />
</settings>
statement缓存开关
personMapper.java
@Options(useCache = true)
Person getPersonById(String id);
PersonMapper.xml
<select id="getPersonById" resultMap="BaseResultMap" useCache="true">
清空缓存
默认修改语句后清空缓存,查询不清空缓存
personMapper.java
@Options(flushCache = Options.FlushCachePolicy.TRUE)
Person getPersonById(String id);
PersonMapper.xml
<select id="getPersonById" resultMap="BaseResultMap" flushCache="true">
声明缓存空间
personMapper.java
@CacheNamespace
public interface PersonMapper {
Person getPersonById(String id);
Person getPersonById2(String id);
@Select("select * from person where id = #{id}")
@Options(flushCache = Options.FlushCachePolicy.TRUE)
Person getPersonById3(String id);
void updatePersonNameById(@Param("id") String id, @Param("name") String name);
}
PersonMapper.xml
<cache
eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size="512"
readOnly="true"/>
引用缓存空间
personMapper.java
@CacheNamespaceRef(BlogMapper.class)
public interface PersonMapper {
Person getPersonById(String id);
Person getPersonById2(String id);
@Select("select * from person where id = #{id}")
@Options(flushCache = Options.FlushCachePolicy.TRUE)
Person getPersonById3(String id);
void updatePersonNameById(@Param("id") String id, @Param("name") String name);
}
PersonMapper.xml
<cache-ref namespace="com.laoxu.mybatis.mapper.BlogMapper"/>
级缓存源码分析
为什么要提交之后才能命中缓存?
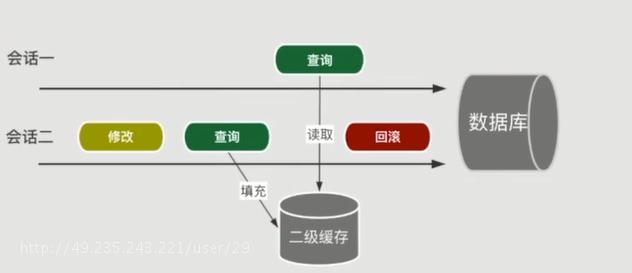
会话二进行修改并查询填充二级缓存成功,二级缓存中含有此次查询的数据,这时候会话一进行查询时发现有二级缓存,那么就直接拿缓存中的数据,但是,如果此时会话二回滚后,那么数据库中的数据没有被修改掉,那么存在二级缓存的数据就是错误的,就会造成脏读。所以必须提交后才可命中缓存
二级缓存空间
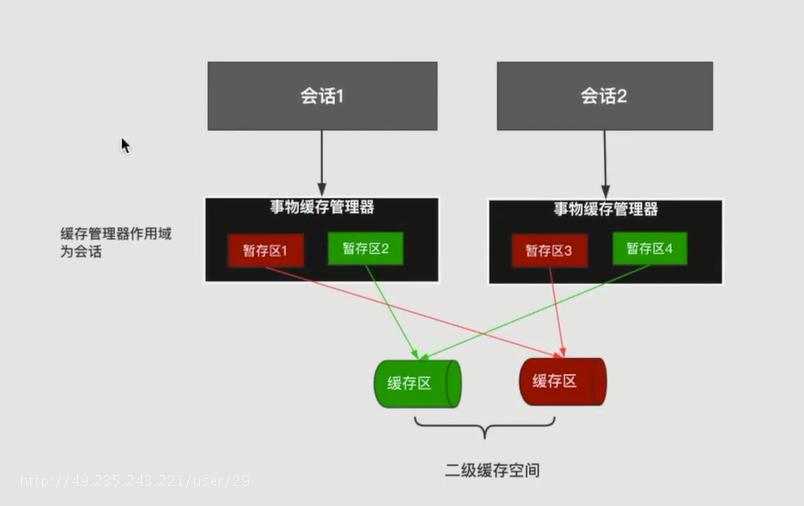
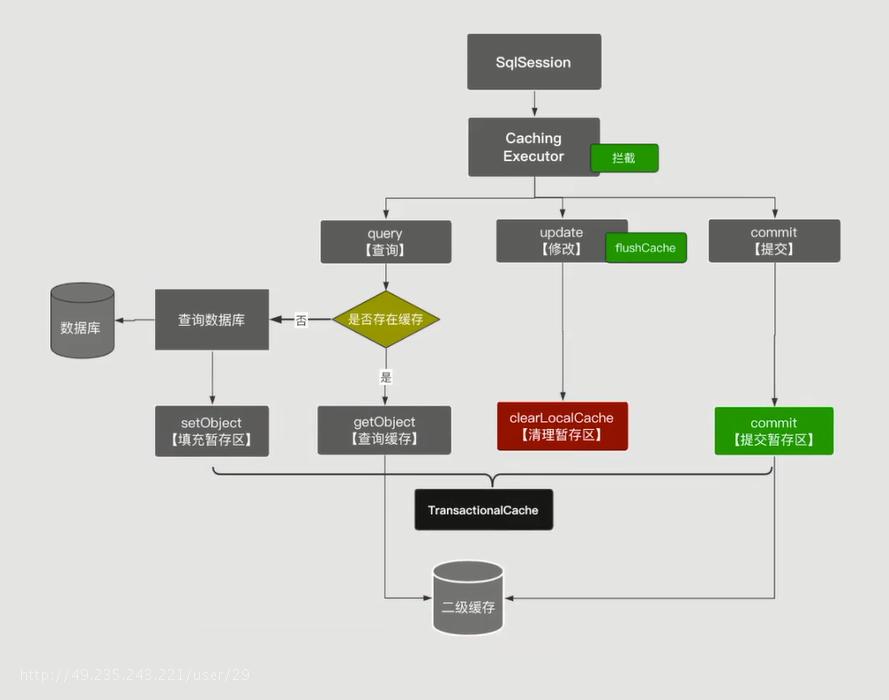
trasactionalCaches为暂存区缓存,还不是真正的二级缓存,只有提交commit()后才会填充到真正的二级缓存
com.laoxu.mybatis.mapper.PersonMapper 对应它的一个暂存区和它的一个缓存区
com.laoxu.mybatis.mapper.BlogMapper 对应它的一个暂存区和它的一个缓存区
二级缓存的存取流程
TransactionalCache就是暂存区
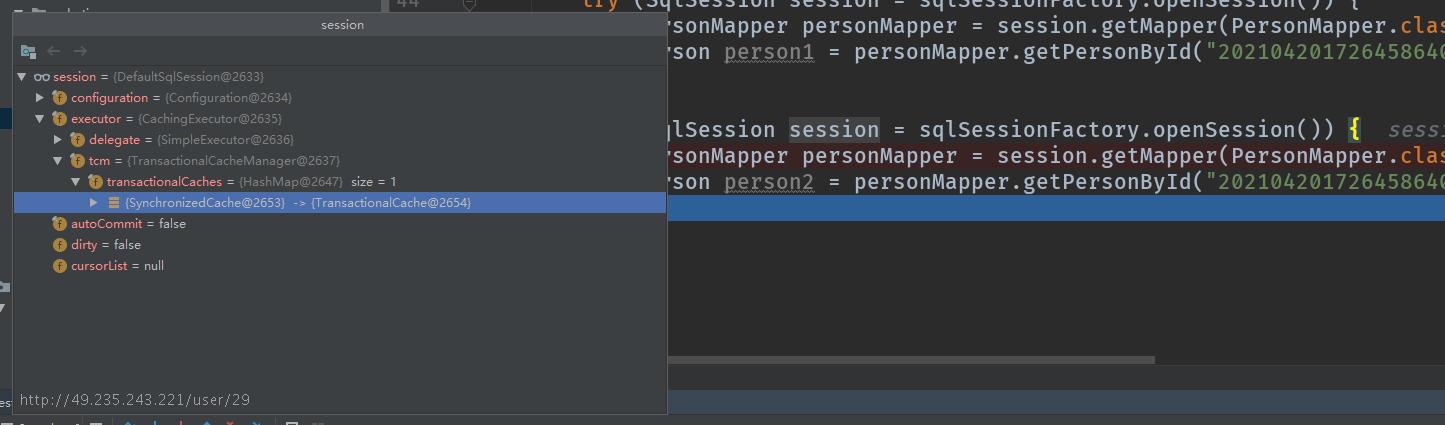
执行查询调试:
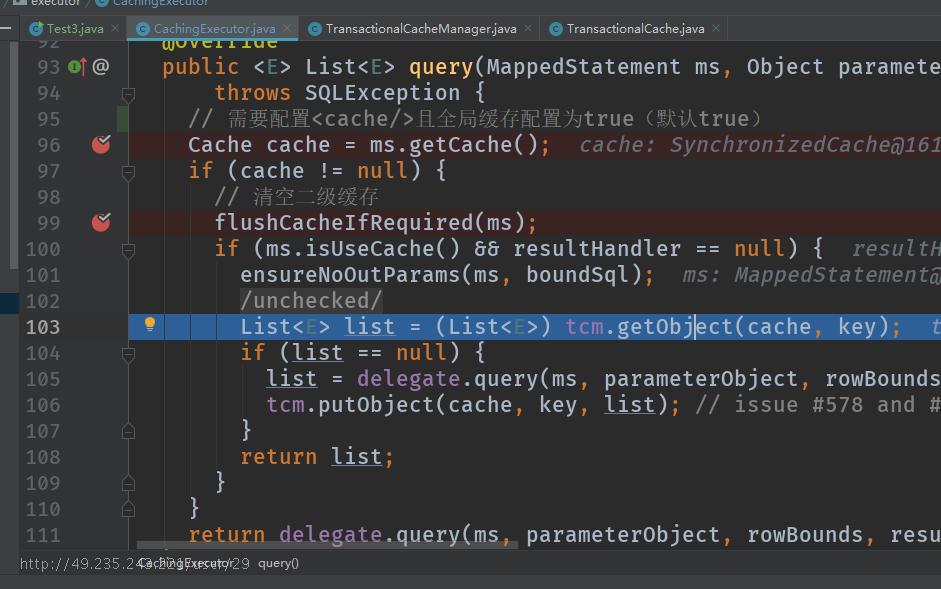
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 需要配置<cache/>且全局缓存配置为true(默认true)
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
// 清空暂存区
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
清空暂存区:
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
public void clear(Cache cache) {
getTransactionalCache(cache).clear();
}
@Override
public void clear() {
clearOnCommit = true;
entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
}
clearOnCommit 清空标志设为true
entriesToAddOnCommit 并且清空暂存区
需要传入cache寻找对应的暂存区:
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) {
return getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key);
}
private TransactionalCache getTransactionalCache(Cache cache) {
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(transactionalCaches, cache, TransactionalCache::new);
}
private final Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> transactionalCaches = new HashMap<>();
传入的Cache作为key去获取TransactionalCache暂存区
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) {
return getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key);
}
第一次查询
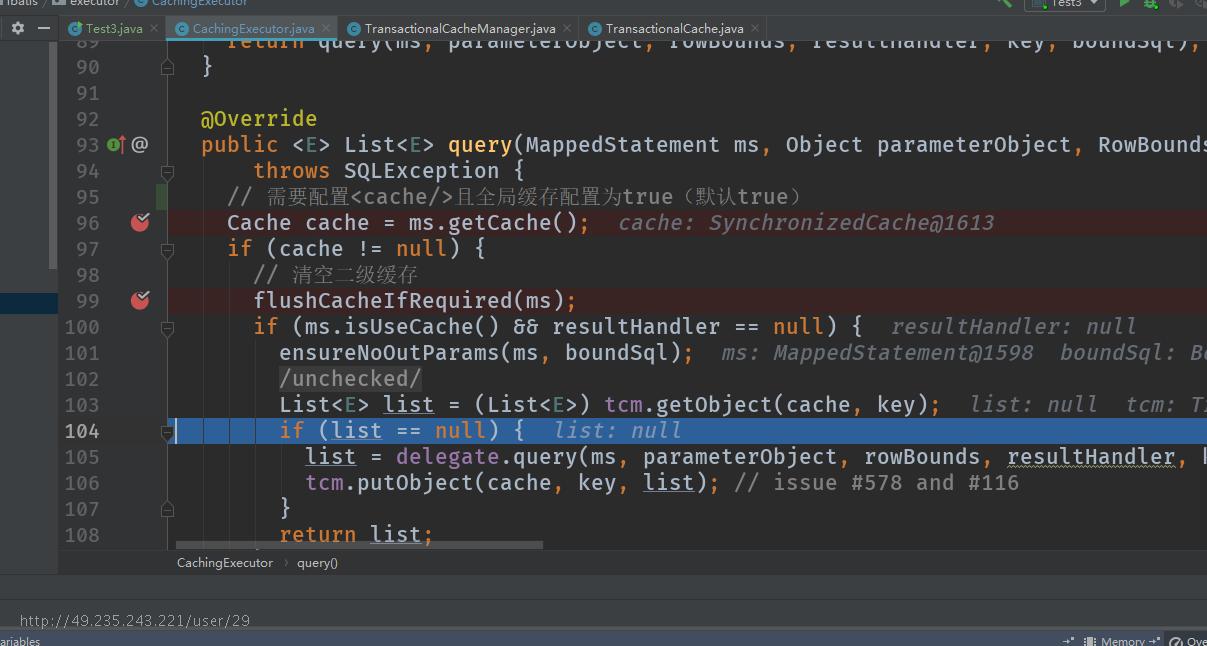
第一次查询到缓存为空,则查询数据库,将查询的结果添加到暂存区
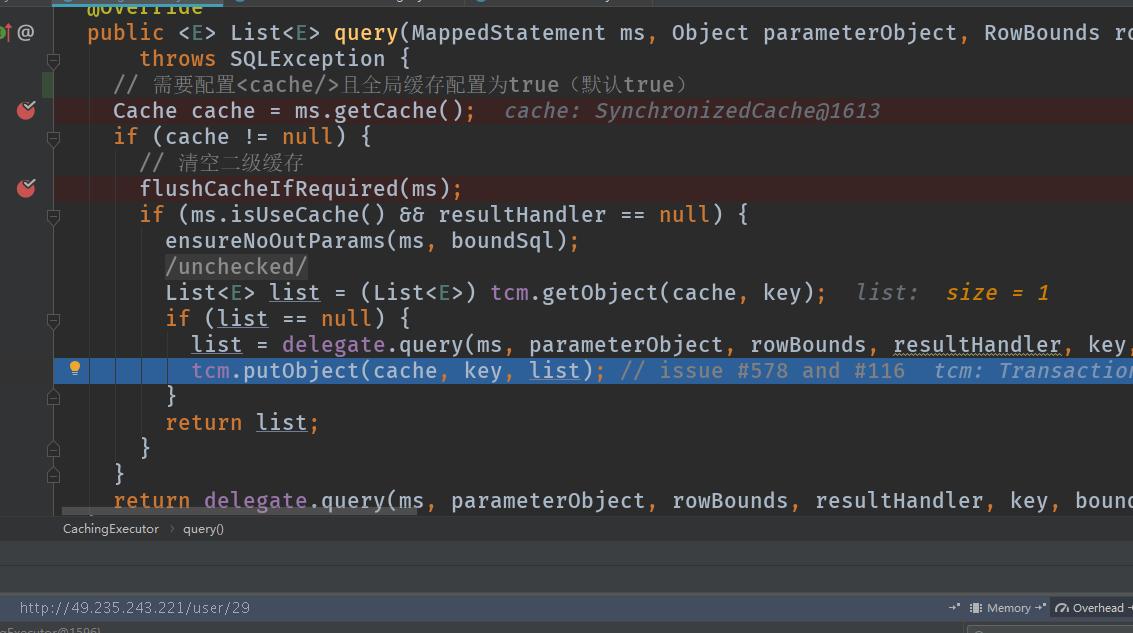
public void putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) {
getTransactionalCache(cache).putObject(key, value);
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object object) {
entriesToAddOnCommit.put(key, object);
}
private final Map<Object, Object> entriesToAddOnCommit;
entriesToAddOnCommit暂存区Map
第二次查询:
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) {
return getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key);
}
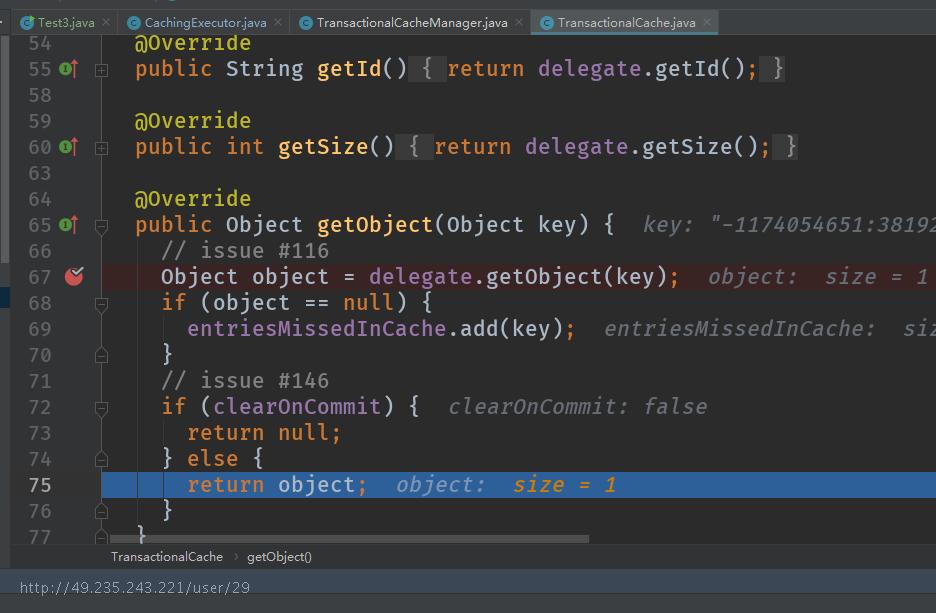
private final Cache delegate;
Object object = delegate.getObject(key);
直接去二级缓存delegate中获取缓存的数据
当有commit()提交后,二级缓存会被全部清除
update、delete等操作会提交事务
public void commit() {
if (clearOnCommit) {
delegate.clear();
}
flushPendingEntries();
reset();
}
如果clearOnCommit为true那么清空所有二级缓存
clearOnCommit为true的清空
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
 mybatis源码-二级缓存
mybatis源码-二级缓存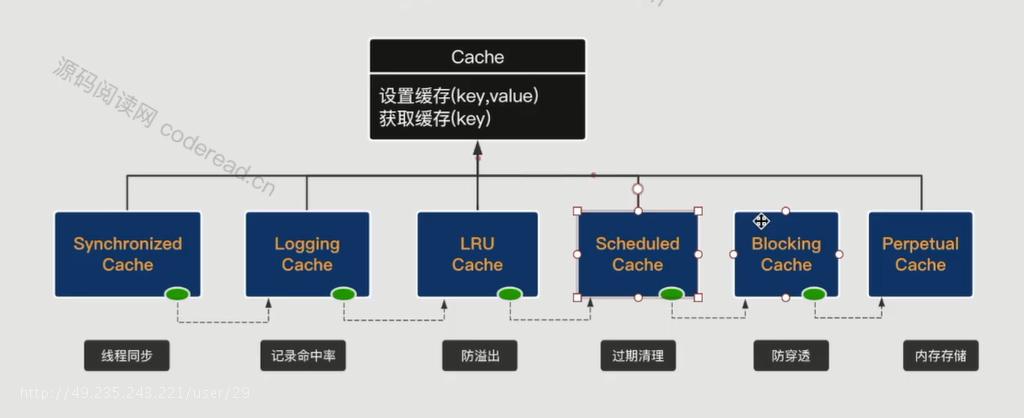
 恭喜注册成功,快来登录吧!
恭喜注册成功,快来登录吧!